THIS INFORMATION IS FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS ONLY
Proximal humeral fractures account
for 10% of all bone fractures
They are the third most frequent fracture in elderly people after hip fracture
and distal forearm fracture.
- More than 70% of patients with a proximal humeral fracture are older than 60 years
- About 75% are women
- From 40 years of age the risk of fracture begins to increase exponentially
The evaluation and management of these injuries is often controversial
and there is neither a general consensus nor a fully satisfying treatment. *
The use of a dedicated external fixator is a valuable option for the treatment of proximal humeral fractures
Similar benefits
to those of traditional pinning technique *
Better biomechanical characteristics *
Good clinical outcomes and a 3% revision rate *
Complete the form now!
Please read our Privacy Policy before submitting this form
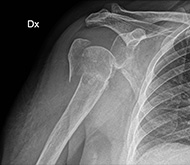
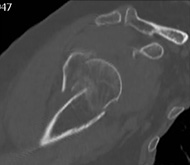
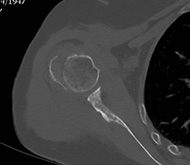
Varus displaced proximal humeral fracture treated with Galaxy Fixation Shoulder
80 year-old male patient Cause of injury: fall on the left shoulder
At presentation he had pain and complete functional impairment. He was neurovascularly intact.
The CT scan showed a significant impaction of the humeral head, a medialization of the shaft with internal rotation of the humeral head.
The patient was generally fit and active and a surgical intervention with closed reduction and fixation with Galaxy Shoulder was suggested in order to reduce the fracture, increase the chance of anatomical healing, and provide a faster return to the activity of daily living.
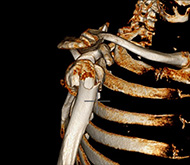
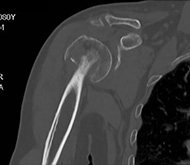
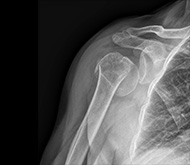
Displaced humeral head and greater tuberosity treated with
Galaxy Fixation Shoulder
70 year-old female patient
Cause of injury: fall on the right shoulder
At presentation she had pain and complete functional impairment. She was neurovascularly intact.
The X-ray showed a displaced humeral head and greater tuberosity. The CT scan showed a valgus-displaced proximal humeral fracture.
The patient was affected by rheumatoid arthritis. Surgical intervention was proposed and scheduled 4 days after the trauma. An open reduction using a deltopectoral approach was performed to reduce the fracture.
Complete the form now!
Please read our Privacy Policy before submitting this form
Question | Answear | Category |
a) Which is the patients’ feedback about the external fixator on their shoulder? | a-b) KOLs spend quite an amount of time before surgery explaining to the patient the benefits of the external fixator. A well-prepared patient is the key for a good compliance with the post-op recovery. The majority of the patients understand that 6 weeks of external fixator is a cheap price to pay compared to the very low complication rate, especially the very low revision rate. At follow up examination, it is uncommon that patients report the 6 weeks of life with the external fixator as a very bad experience. | a-b) Patient compliance |
Could you perform surgery with local anesthesia or neural block ? | In old patients with comorbidities the anesthesiologists prefer peripheral block instead of general anesthesia. This is especially true in case of 2 part PHF, in which the risk of intraoperative conversion to a replacement is extremely low | Anesthesia |
Have you ever faced damages to axillary nerve with this technique? | Not with the last version of our “pins bridging fracture technique”. With the old technique, in which KOLS adopted more oblique wires, they observed one temporary partial palsy, that resolved within 6 months follow up | Axillary Nerve |
Are there review articles about this approach? | There are no studies available yet comparing all different techniques | Comparison |
In young patients, do you prefer plating or nailing for better reduction? | Galaxy Shoulder Fixation System is a tool for fixation not for reduction. Being a tool for fixation, we cannot blame it for a bad reduction. Similarly, when we face bad reductions after fracture fixation with a plate or a nail, we blame the surgeon and not the tool. For the same reason, our KOLs suggest an open reduction and a percutaneous fixation if the reduction is not satisfactory after closed manoeuvres | Comparison |
Have you experienced any conversions to e.g. plating or replacement? | KOLs have limited experience of intraoperative conversion to a reverse replacement. The rate of infection is probably higher than a reverse replacement in a pristine shoulder. For this reason, they recommend, in the most complicated cases, to start directly with open reduction, without the use of any percutaneous pins. If the surgeon is able to obtain a temporary satisfactory reduction, he/she can proceed with the percutaneous fixation. If this is not the case, the surgeon is suggested to change the indication as soon as possible. | Complications |
In your experience have you never had a case of osteonecrosis after this treatment? | Yes. Our KOLs rate of AVN (at a minimum follow up fo 2 y) is under 4%. Rarely these patients required additional surgery, due to the absence of metalware like locking screws causing glenoid erosion and pain | Complications |
What about articular glenoid impingement or condral damage of first two humeral head distal pins extremity? | The surgeon must check the length of the pins. There are ways that can guarantee the safety of this procedure. First of all the surgeon must check visually the length of the pins putting the shoulder in internal and external rotation. Secondly, after the insertion of pins, the surgeon has to move the shoulder and detect any clue of protruding pins (crepitus, locking etc etc). In the worst scenario, the surgeon fails to detect a protruding pin, but considering that after 6 weeks everything is removed, the risk of damaging the glenoid is very low and probably not clinically relevant. | Complications |
What kind of complications have you had? | KOLs had some complications with this technique, such as avascular necrosis or non-union. The benefit of this technique is that the majority of the potential complications can be treated conservatively. The proof of that lies in our rate of revision surgery, only 3% (Follow-up Ranging from 2 to 12 Years). | Complications |
Have you ever experienced pin tract infection? | Our KOLs rate of pin tract infection is around 8%. All these infections were treated by 7 to 14 days of oral antibiotics. None of the pin tract infections evolved in a deep infection. In none of the cases they changed their plan due to a pin tract infection, including earlier removal of the infected pin. | Complications |
Have you ever had fracture sequelae with this treatment? | Our KOLs had some complications with this technique. The benefit of this technique is that the majority of the potential complications can be treated conservatively. The proof of that lies in our KOLs rate of revision surgery, only 3% (Follow-up Ranging from 2 to 12 Years) | Complications |
What do you do in case of secondary displacement? | Since KOLs have introduced the “pins-bridging technique” they haven’t recorded any significant secondary displacement. This positive outcome is probably the combination of several factors, including the good biomechanical features of the dedicated external fixator, the right selection of the patients, and the surgeon’s experience. A secondary displacement of the fracture should anyway have a similar treatment of another fixation tool. If an early failure is thought to be related to a wrong technique (bad reduction, pins badly positioned in the humeral head, etc), the surgeon can try to apply again the external fixator correcting the technique. If the failure is related to the patient, i.e. recurrent trauma with a secondary displacement of the fracture, they recommend conservative treatment. | Loss of reduction |
Have you ever had loss of reduction in osteoporotic humeral heads? | The loosening or backing out of the threaded wires is an extremely rare event. Our KOLs did record this complication but only in 2 patients that the night of the surgery, fell from the bed, during a severe episode of delirium. For this reason, they have learned to contraindicate this technique to patients with very poor compliance or suffering severe neurological disease, which puts them at risk of early fall. They never did a second surgery for loss of reduction, by using this technique. This is also true for patients affected by poor bone quality in which loss of reduction is an extremely rare event. Theoretically, this complication, can be managed either by re-doing the fixation with the external fixator (if the surgeon believes that the fixator was placed in a suboptimal position) or changing fixation device. In this regard, Dr Blonna does not think that changing the device gives better biomechanical advantages than an external fixator placed correctly. Moreover, the great benefit of a temporary device, such as the Galaxy Shoulder Fixation System, is that the patient can cope easily with a minor degree of secondary displacement because after 40 days the ex-fix is removed with no risk of screws cutting out and erosion of the glenoid. | Loss of Reduction |
During treatment, have oblique wires ever migrate into the shoulder joint? | No. Since the external fixator is removed around 40 days from the surgery, the migration of the wires in the joint can’t occur. The mobilization of the wires was much more common in the other direction (with wires backing out and loosening of the reduction) by using standard K-wires without external fixator. After the introduction of the dedicate external fixator threaded wires we solved completely this otherwise common complication. | Loss of Reduction |
Do you change wrappings and how do you clean the pins? | Wound care once a week | Post op protocol |
The plate is more investigated with greater blood loss compared to a minimally invasive approach, but rapid mobilisation is provided anyway. What do you think about it? | In our KOLs experience, the average old patient affected by 3 to 4 part PHF, treated with a plate or a nail, does not resume the activity of daily life very soon, despite surgeon post-op suggestions. In young patients, it is easier regardless of the tool you might use. The limiting factor is usually the pain. Our KOLs belief, supported by some experience coming from hospitals that are still using plate along with the external fixator, is that the treatment with the external fixator could provide a faster return to activity of daily life due to less pain and stiffness. | Rehabilitation |
How long do your patients wait for starting rehabilitation? | A self-assisted pendulum exercise is started as soon as possible (usually 5 to 7 days after surgery). A formal rehab program, with a physiotherapist, is usually started 3 to 4 weeks after surgery. Younger patients start the rehab program 10 days -2 weeks after surgery. | Rehabilitation |
Is it immediately possible to mobilize the arm after surgery? | In young patients, KOLs suggest an early rehabilitation, starting passive ROM immediately after surgery and removing the sling according to the pain. | Rehabilitation |
Could it be useful to remove only greater tuberosity wires at week 4? | This can be an option to speed up rehabilitation or to solve pins tract infection, but our KOLs don’t have experience in this practice. | Removal |
How do you maintain the reduction during first wire insertion? | Usually, keeping the patient’s arm still is enough to avoid intraoperative displacements. This is true especially in the case of 2 part PHF after closed reduction. In the case of an open procedure, the reduction is maintained by the blunt instrument. To reduce the time lapse between reduction and fixation KOLs prefer to start preparing the two obliques pins even if the head is still displaced. When the pins are in place, the reduction of the humeral head is immediately followed by the further insertion of the two pins. In this way the risk of intraoperative displacement is extremely low. | Surgery |
Do you never control the profile on X ray? | Maximum internal rotation and external rotation are more than enough to be sure about reduction and length of pins | Surgery |
How far from the fracture do you have to insert distal wires? | Our KOLs suggestion is 2 to 4 centimeters distal from the oblique pins. Avoiding to stay too close to the oblique pins should limit the risk of iatrogenic fracture | Surgery |
In the case of 2-3 fragments, would it have been better to put a plate and still run an open access for fracture reduction? | Dr Blonna has just published a paper on JBJS in which his rate of revision surgery (of any type) is below 5%, with a minimum follow up of 2 years. Approximately half of the patients suffered of 3-4 part PHF -hence difficult cases. Despite he didn’t have a control group treated with a plate, the literature suggests that the revision rate using plates is higher than 10%. Strong of his experience and data, he has stopped using plates since 10 years. | Surgery |
In which type of fractures do you find most difficult to decide between intramedullary nailing and external fixation osteosynthesis? | KOLs have abandoned other fixation devices, confident by their results using the external fixator. Having said that, in case of fracture of 1 cm distal to the surgical neck, they would consider a plate or a nail because it is difficult to insert the 2 oblique pins when the fracture is too distal. | Surgery |
In case of fracture with more fragments in which you choose orif, do you also use osteosutures in addition to the pins? | Yes, our KOLs normally link GT and LT together with number 2 non-absorbable sutures | Surgery |
Why not using a first proximal pin percutaneously to do a close reduction before ascendant pins? | If the fracture is very unstable (a not very common event) and the patient is not fat or muscular, the 2 proximal pins can be used to reduce the humeral head or/and the GT. However the pins are not designed for this purpose. The surgeon should be aware of the potential breakage of pins. Moreover, a bent pin is difficult to be removed without anestesia. The lesser tuberosity, if displaced (not just broken) is reduced and fixed with osteosutures using a deltopectoral approach | Surgery |
Is it possible to add other pins if fracture requires? | Yes it is possible. The external fixator can be used as well. This was a common event in our KOLs early experience. The principle of using only 6 pins, is to propose a standardized and reliable technique. If the surgeon is not sure about the position of one of the pins, an additional pin can be placed. On the contrary, we discourage surgeons to use less than 6 pins. | Surgery |
To treat a 3 part proximal humeraus fracture (but even 2 part) with the common varus and posterior head comminution, the close reduction is performed in ABD and RE, pushing the diaphysis posteriorly. The introduction of the wires in such position, kept by an assistant, follows always the same procedure: 1 cm anteriorly to the middle line of the humerus and 9 cm distally the lateral edge of the acromium? | Of course it’s not easy. The best way to insert the oblique wires is relying on the landmarks and aiming posteriorly. If a good reduction has been achieved, the humeral head will be 20°-30° in a retroversal position.In case of doubt, inserting the pin more anteriorly will allow to get a better posterior position. The coracoid is another reference point. In normal conditions, the coracoid point shuould be projected in the middle of the humeral head. Once got the reduction, it is possible to keep the shoulder in a more phyological position and not in ABD and ER. Usually our KOLs keep the shoulder in a neutral position at 20°-30° of abduction. | Surgery |
How long is X-ray exposure for a complete surgery? | The exposure to X-rays depends on several factors including the type of fracture and surgeon skills. A simple 2 part proximal humeral fracture required less than 20 seconds. The most difficult cases usually less than 1 minute. The open procedure reduces substantially the amount of X-rays. | Surgery |
Do you prefer lateral or Beach chair position? | Beach chair position | Surgery |
What is the average length of surgery time? | In our KOLs experience, the majority of surgeries last less than 1h. The easiest cases can be treated in 20 minutes. | Surgery |
Is it mandatory to perform the reduction with close manoeuvers? | In case of 4-part proximal humeral fracture, KOLs recommend an open reduction. In case of 3-part proximal humeral fracture and 2-part proximal humeral fracture, the type of reduction depends on what the surgoen is achieving by closed manoeuvers. If he obtains a satisfactory reduction of the fragments by closed manoeuvers, this would give better cosmesis, less pain and less deep infections than a standard open procedure. If the reduction is not satisfactory after an attempt for closed reduction, KOLS’ threshold to change from closed to open is very low. In simple terms, a satisfactory open reduction is better than an unsatisfactory closed reduction. The open reduction and percutaneous fixation by using the Galaxy Shoulder Fixator technique increase the rate of deep infection compared to closed reduction but not compared to a standard open reduction and internal fixator by using a plate or nail. These data have been published in a multicentre study. | Surgery |
After how many minutes do you decide to “switch” to open reduction? | In case of a true 4-part proximal humeral fracture (lesser tuberosity is displaced not only fractured), KOLs recommend an open reduction without an attempt for closed reduction. In case of 3-part proximal humeral fracture and 2-part proximal humeral fracture, the type of reduction depends on what we are achieving by closed manoeuvers. If by closed manoeuvers the surgeon obtains a satisfactory reduction of the fragments this would give better cosmesis, less pain and less deep infections than a standard open procedure. If the reduction is not satisfactory after an attempt for closed reduction, our KOLs threshold to change from closed to open is very low and they swift to an open reduction in about 10 to 20 minutes usually. | Surgery |
Do you use wires to help reduction? | This option can be used to improve the quality of the reduction. However, the threaded wires are not designed to support aggressive reduction manoeuvers. Moreover, the quality of the bone at the level of the greater tuberosity can determine the fragmentation of the greater tuberosity during reduction manoeuvers. KOLs suggest not to use this technique routinely. | Surgery |
Is it always helpful to dis-impact the humeral head in three part valgus impacted fractures? | Our aim is to obtain a good reduction of the humeral head. Valgus impacted proximal humeral fractures usually are associated with satisfactory results after conservative treatment. If surgical treatment is indicated, the surgeon should aim for a reduction of the humeral head. | Surgery |
Which is the percentage of open reduction when using this product? | In our KOLs last report on JBJS on 188 patients, the reduction was performed with percutaneous manoeuvers in 120 shoulders (63.8%) and with delto-pectoral approach in 68 cases (36.2%). | Surgery |
Is it effective for osteoporotic bone? | The “pins-bridging fracture technique” and the Galaxy Shoulder external fixator have been designed to be used regardless of the quality of the bone. Thanks to the concept of bi-cortical fixation and to an external fixator dedicated to the treatment of proximal humeral fracture, satisfactory outcomes can be achieved in either young and old patients. This is also true in case of patients affected by poor bone quality where loss of fracture reduction is an extremely rare event. | System |
What is the longest time you can wait to fix a fracture with external fixation? | It depends on the fracture. If the fracture is unstable and a secondary displacement is diagnosed at 2/3 weeks from trauma, an attempt for closed reduction and fixation with Galaxy can be performed. If closed reduction is not achievable, a good solution is always an open reduction followed by a percutaneous fixation using the Galaxy. | System |
What are the real advantages of using external fixation? | 1) It is a temporary fixation so lower risk of delayed complications related to hardware. | System |
Is the fixator compatible with magnetic resonance? | No, it isn’t | System |
Which is the diameter of the K. wires? | 2.5 mm | System |
Is there a standard way to connect the 6 wires together? | Yes, the technique is reported in the official brochure. Having said that, changes can be done in order to connect the 6 wires. The concept is that all threaded wires have to be linked to the rods. | System |
What movement has the middle node (clamp)? | The system is designed to have a great level of freedom. Depending on the positioning of the pins and the length of the rods the middle node (clamp) can be linked to each rod segment and a 360° orientation | System |
| Question | Answer |
| In young patients, do you prefer plating or nailing for better reduction? | Galaxy Shoulder Fixation System is a tool for fixation not for reduction. Being a tool for fixation, we cannot blame it for a bad reduction. Similarly, when we face bad reductions after fracture fixation with a plate or a nail, we blame the surgeon and not the tool. For the same reason, our KOLs suggest an open reduction and a percutaneous fixation if the reduction is not satisfactory after closed manoeuvres |
| In which type of fractures do you find most difficult to decide between intramedullary nailing and external fixation osteosynthesis? | KOLs have abandoned other fixation devices, confident by their results using the external fixator. Having said that, in case of fracture of 1 cm distal to the surgical neck, they would consider a plate or a nail because it is difficult to insert the 2 oblique pins when the fracture is too distal. |
| The plate is more investigated with greater blood loss compared to a minimally invasive approach, but rapid mobilisation is provided anyway. What do you think about it? | In our KOLs experience, the average old patient affected by 3 to 4 part PHF, treated with a plate or a nail, does not resume the activity of daily life very soon, despite surgeon post-op suggestions. In young patients, it is easier regardless of the tool you might use. The limiting factor is usually the pain. Our KOLs belief, supported by some experience coming from hospitals that are still using plate along with the external fixator, is that the treatment with the external fixator could provide a faster return to activity of daily life due to less pain and stiffness. |
| Are there review articles about this approach? If so, what are their conclusions vs plating, nailing, pinning? | There are no studies available yet comparing all different techniques |
| Question | Answer |
| What kind of complications have you had? | KOLs had some complications with this technique, such as avascular necrosis or non-union. The benefit of this technique is that the majority of the potential complications can be treated conservatively. The proof of that lies in our rate of revision surgery, only 3% (Follow-up Ranging from 2 to 12 Years). |
| Have you ever experienced pin tract infection? | Our KOLs rate of pin tract infection is around 8%. All these infections were treated by 7 to 14 days of oral antibiotics. None of the pin tract infections evolved in a deep infection. In none of the cases they changed their plan due to a pin tract infection, including earlier removal of the infected pin. |
| In your experience have you never had a case of osteonecrosis after this treatment? | Yes. Our KOLs rate of AVN (at a minimum follow up fo 2 y) is under 4%. Rarely these patients required additional surgery, due to the absence of metalware like locking screws causing glenoid erosion and pain |
| Have you ever had loss of reduction in osteoporotic humeral heads? If yes, which is the rate? | The loosening or backing out of the threaded wires is an extremely rare event. Our KOLs did record this complication but only in 2 patients that the night of the surgery, fell from the bed, during a severe episode of delirium. For this reason, they have learned to contraindicate this technique to patients with very poor compliance or suffering severe neurological disease, which puts them at risk of early fall. They never did a second surgery for loss of reduction, by using this technique. This is also true for patients affected by poor bone quality in which loss of reduction is an extremely rare event. Theoretically, this complication, can be managed either by re-doing the fixation with the external fixator (if the surgeon believes that the fixator was placed in a suboptimal position) or changing fixation device. In this regard, Dr Blonna does not think that changing the device gives better biomechanical advantages than an external fixator placed correctly. Moreover, the great benefit of a temporary device, such as the Galaxy Shoulder Fixation System, is that the patient can cope easily with a minor degree of secondary displacement because after 40 days the ex-fix is removed with no risk of screws cutting out and erosion of the glenoid. |
| What do you do in case of secondary displacement? how often do you do a check x-ray? | Since KOLs have introduced the “pins-bridging technique” they haven’t recorded any significant secondary displacement. This positive outcome is probably the combination of several factors, including the good biomechanical features of the dedicated external fixator, the right selection of the patients, and the surgeon’s experience. A secondary displacement of the fracture should anyway have a similar treatment of another fixation tool. If an early failure is thought to be related to a wrong technique (bad reduction, pins badly positioned in the humeral head, etc), the surgeon can try to apply again the external fixator correcting the technique. If the failure is related to the patient, i.e. recurrent trauma with a secondary displacement of the fracture, they recommend conservative treatment. |
| During treatment, have oblique wires ever migrate into the shoulder joint? | No. Since the external fixator is removed around 40 days from the surgery, the migration of the wires in the joint can’t occur. The mobilization of the wires was much more common in the other direction (with wires backing out and loosening of the reduction) by using standard K-wires without external fixator. After the introduction of the dedicate external fixator threaded wires we solved completely this otherwise common complication. |
| Have you ever had fracture sequelae with this treatment? | Our KOLs had some complications with this technique. The benefit of this technique is that the majority of the potential complications can be treated conservatively. The proof of that lies in our KOLs rate of revision surgery, only 3% (Follow-up Ranging from 2 to 12 Years) |
| What is your rate of union vs non-union and delayed union? | Non-union rate 0.5% (1 case). AVN 4%. Revision surgery rate 3%. |
| Have you experienced any conversions to e.g. plating or replacement? Any infectious complications? | KOLs have limited experience of intraoperative conversion to a reverse replacement. The rate of infection is probably higher than a reverse replacement in a pristine shoulder. For this reason, they recommend, in the most complicated cases, to start directly with open reduction, without the use of any percutaneous pins. If the surgeon is able to obtain a temporary satisfactory reduction, he/she can proceed with the percutaneous fixation. If this is not the case, the surgeon is suggested to change the indication as soon as possible. |
| Have you had any cases of chondrolysis or glenohumeral arthrosis related to the intrarticular wires? | No |
| What about articular glenoid impingement or condral damage of first two humeral head distal pins extremity? | The surgeon must check the length of the pins. There are ways that can guarantee the safety of this procedure. First of all the surgeon must check visually the length of the pins putting the shoulder in internal and external rotation. Secondly, after the insertion of pins, the surgeon has to move the shoulder and detect any clue of protruding pins (crepitus, locking etc etc). In the worst scenario, the surgeon fails to detect a protruding pin, but considering that after 6 weeks everything is removed, the risk of damaging the glenoid is very low and probably not clinically relevant. |
| Question | Answer |
| Which is the patients’ feedback about the external fixator on their shoulder ? Before the surgery, just after the surgery ? | KOLs spend quite an amount of time before surgery explaining to the patient the benefits of the external fixator. A well-prepared patient is the key for a good compliance with the post-op recovery. The majority of the patients understand that 6 weeks of external fixator is a cheap price to pay compared to the very low complication rate, especially the very low revision rate. At follow up examination, it is uncommon that patients report the 6 weeks of life with the external fixator as a very bad experience. |
| Is it effective for osteoporotic bone? | The “pins-bridging fracture technique” and the Galaxy Shoulder external fixator have been designed to be used regardless of the quality of the bone. Thanks to the concept of bi-cortical fixation and to an external fixator dedicated to the treatment of proximal humeral fracture, satisfactory outcomes can be achieved in either young and old patients. This is also true in case of patients affected by poor bone quality where loss of fracture reduction is an extremely rare event. |
| What is the longest time you can wait to fix a fracture with external fixation? Is 14 days too long? | It depends on the fracture. If the fracture is unstable and a secondary displacement is diagnosed at 2/3 weeks from trauma, an attempt for closed reduction and fixation with Galaxy can be performed. If closed reduction is not achievable, a good solution is always an open reduction followed by a percutaneous fixation using the Galaxy. |
| Question | Answer |
| Do you have a patient protocol ? | Wound care once a week. In young patients, KOLs suggest an early rehabilitation, starting with passive ROM immediately after surgery and removing the sling according to the pain. In old patients with complex fractures, KOLs suggest a more conservative rehab protocol. If this is the case, KOLs suggest a gentle pendulum exercises a few days after surgery, but active ROM is recommended only after the removal of the external fixator. If the surgeon is in doubt about when starting passive and active ROM after surgery, the opinion of the developers of the Galaxy Shoulder Fixation System is that a delayed rehab, in their long experience, does not affect negatively the final outcome. So, if in doubt, do not push too much on early rehabilitation. |
| Is it immediately possible to mobilize the arm after surgery? | In young patients, KOLs suggest an early rehabilitation, starting passive ROM immediately after surgery and removing the sling according to the pain. In old patients with complex fracture, KOLs suggest a more conservative rehab protocol. If this is the case, we can start with gentle pendulum exercises a few days after surgery, but active ROM is recommended after the removal of the external fixator. If the surgeon is in doubt about when starting passive and active ROM after surgery, the opinion of the developers of the Galaxy Shoulder Fixation System is that a delayed motion, in their long experience, do not affect negatively the final outcome. So, if in doubt, do not push too much on early rehabilitation. |
| How long do your patients wait for starting rehabilitation? | A self-assisted pendulum exercise is started as soon as possible (usually 5 to 7 days after surgery). A formal rehab program, with a physiotherapist, is usually started 3 to 4 weeks after surgery. Younger patients start the rehab program 10 days -2 weeks after surgery. |
| Do you change wrappings and how do you clean the pins? | Wound care once a week |
| Could it be useful to remove only greater tuberosity wires at week 4? | This can be an option to speed up rehabilitation or to solve pins tract infection, but our KOLs don’t have experience in this practice. |
| Have you ever faced damages to axillary nerve with this technique? | Not with the last version of our “pins bridging fracture technique”. With the old technique, in which KOLS adopted more oblique wires, they observed one temporary partial palsy, that resolved within 6 months follow up |
| Question | Answer |
| What is the average length of surgery time? | In our KOLs experience, the majority of surgeries last less than 1h. The easiest cases can be treated in 20 minutes. |
| Is it mandatory to perform the reduction with close manoeuvers? | In case of 4-part proximal humeral fracture, KOLs recommend an open reduction. In case of 3-part proximal humeral fracture and 2-part proximal humeral fracture, the type of reduction depends on what the surgoen is achieving by closed manoeuvers. If he obtains a satisfactory reduction of the fragments by closed manoeuvers, this would give better cosmesis, less pain and less deep infections than a standard open procedure. If the reduction is not satisfactory after an attempt for closed reduction, KOLS’ threshold to change from closed to open is very low. In simple terms, a satisfactory open reduction is better than an unsatisfactory closed reduction. The open reduction and percutaneous fixation by using the Galaxy Shoulder Fixator technique increase the rate of deep infection compared to closed reduction but not compared to a standard open reduction and internal fixator by using a plate or nail. These data have been published in a multicentre study. |
| Do you use wires to help reduction? | This option can be used to improve the quality of the reduction. However, the threaded wires are not designed to support aggressive reduction manoeuvers. Moreover, the quality of the bone at the level of the greater tuberosity can determine the fragmentation of the greater tuberosity during reduction manoeuvers. KOLs suggest not to use this technique routinely. |
| Is it always helpful to dis-impact the humeral head in three part valgus impacted fractures? | Our aim is to obtain a good reduction of the humeral head. Valgus impacted proximal humeral fractures usually are associated with satisfactory results after conservative treatment. If surgical treatment is indicated, the surgeon should aim for a reduction of the humeral head. |
| How do you maintain the reduction during first wire insertion? | Usually, keeping the patient’s arm still is enough to avoid intraoperative displacements. This is true especially in the case of 2 part PHF after closed reduction. In the case of an open procedure, the reduction is maintained by the blunt instrument. To reduce the time lapse between reduction and fixation KOLs prefer to start preparing the two obliques pins even if the head is still displaced. When the pins are in place, the reduction of the humeral head is immediately followed by the further insertion of the two pins. In this way the risk of intraoperative displacement is extremely low. |
| Why not using a first proximal pin percutaneously to do a close reduction before ascendant pins? What about lesser tuberosity fixation? | If the fracture is very unstable (a not very common event) and the patient is not fat or muscular, the 2 proximal pins can be used to reduce the humeral head or/and the GT. However the pins are not designed for this purpose. The surgeon should be aware of the potential breakage of pins. Moreover, a bent pin is difficult to be removed without anestesia. The lesser tuberosity, if displaced (not just broken) is reduced and fixed with osteosutures using a deltopectoral approach |
| How far from the fracture do you have to insert distal wires? | Our KOLs suggestion is 2 to 4 centimeters distal from the oblique pins. Avoiding to stay too close to the oblique pins should limit the risk of iatrogenic fracture |
| In the case of 2-3 fragments, would it have been better to put a plate and still run an open access for fracture reduction? | Dr Blonna has just published a paper on JBJS in which his rate of revision surgery (of any type) is below 5%, with a minimum follow up of 2 years. Approximately half of the patients suffered of 3-4 part PHF -hence difficult cases. Despite he didn’t have a control group treated with a plate, the literature suggests that the revision rate using plates is higher than 10%. Strong of his experience and data, he has stopped using plates for 10 years. |
| To treat a 3 part proximal humeraus fracture (but even 2 part) with the common varus and posterior head comminution, the close reduction is performed in ABD and RE, pushing the diaphysis posteriorly. The introduction of the wires in such position, kept by an assistant, follows always the same procedure: 1 cm anteriorly to the middle line of the humerus and 9 cm distally the lateral edge of the acromium? | Of course it’s not easy. The best way to insert the oblique wires is relying on the landmarks and aiming posteriorly. If a good reduction has been achieved, the humeral head will be 20°-30° in a retroversal position.In case of doubt, inserting the pin more anteriorly will allow to get a better posterior position. The coracoid is another reference point. In normal conditions, the coracoid point shuould be projected in the middle of the humeral head. Once got the reduction, it is possible to keep the shoulder in a more phyological position and not in ABD and ER. Usually our KOLs keep the shoulder in a neutral position at 20°-30° of abduction. |
| In case of fracture with more fragments in which you choose orif, do you also use osteosutures in addition to the pins? | Yes, our KOLs normally link GT and LT together with number 2 non-absorbable sutures |
| Is it possible to add other pins if fracture requires? | Yes it is possible. The external fixator can be used as well. This was a common event in our KOLs early experience. The principle of using only 6 pins, is to propose a standardized and reliable technique. If the surgeon is not sure about the position of one of the pins, an additional pin can be placed. On the contrary, we discourage surgeons to use less than 6 pins. |
| After how many minutes do you decide to “switch” to open reduction? | In case of a true 4-part proximal humeral fracture (lesser tuberosity is displaced not only fractured), KOLs recommend an open reduction without an attempt for closed reduction. In case of 3-part proximal humeral fracture and 2-part proximal humeral fracture, the type of reduction depends on what we are achieving by closed manoeuvers. If by closed manoeuvers the surgeon obtains a satisfactory reduction of the fragments this would give better cosmesis, less pain and less deep infections than a standard open procedure. If the reduction is not satisfactory after an attempt for closed reduction, our KOLs threshold to change from closed to open is very low and they swift to an open reduction in about 10 to 20 minutes usually. |
| Which is the percentage of open reduction when using this product? | In case of a true 4-part proximal humeral fracture (lesser tuberosity is displaced not only fractured), KOLs recommend an open reduction without an attempt for closed reduction. In case of 3-part proximal humeral fracture and 2-part proximal humeral fracture, the type of reduction depends on what we are achieving by closed manoeuvers. If by closed manoeuvers the surgeon obtains a satisfactory reduction of the fragments this would give better cosmesis, less pain and less deep infections than a standard open procedure. If the reduction is not satisfactory after an attempt for closed reduction, our KOLs threshold to change from closed to open is very low and they swift to an open reduction in about 10 to 20 minutes usually. |
| Which is the percentage of open reduction when using this product? | In our KOLs last report on JBJS on 188 patients, the reduction was performed with percutaneous manoeuvers in 120 shoulders (63.8%) and with delto-pectoral approach in 68 cases (36.2%). |
| Could you perform surgery with local anesthesia or neural block? | In old patients with comorbidities the anesthesiologists prefer peripheral block instead of general anesthesia. This is especially true in case of 2 part PHF, in which the risk of intraoperative conversion to a replacement is extremely low. |
| How long is X-ray exposure for a complete surgery? | The exposure to X-rays depends on several factors including the type of fracture and surgeon skills. A simple 2 part proximal humeral fracture required less than 20 seconds. The most difficult cases usually less than 1 minute. The open procedure reduces substantially the amount of X-rays. |
| Do you never control the profile on X ray? (except with rotation)? | Maximum internal rotation and external rotation are more than enough to be sure about reduction and length of pins. |
| Do you prefer lateral or Beach chair position? | Beach chair position. |
| Question | Answer |
| What are the real advantages of using external fixation? | 1) It is a temporary fixation so lower risk of delayed complications related to hardware. 2) Mini-invasive technique (periosteum is kept intact with a better chance of rapid healing of the fracture). Soft tissue envelopment, including periosteum, is less damaged by the surgeon providing an intrinsic increase of the stability of the fixation. 3) It allows a bi-cortical fixation, something that is not achievable with other techniques. 4) The two proximal threaded wires in the head are placed to work as a buttress against varus displacement. No other systems have screws that can be placed in the same direction as the 2 proximal wires of our technique. |
| Is there a standard way to connect the 6 wires together? | Yes, the technique is reported in the official brochure. Having said that, changes can be done in order to connect the 6 wires. The concept is that all threaded wires have to be linked to the rods. |
| Is the fixator compatible with magnetic resonance? | No, it isn’t |
| Which is the diameter of the K. wires? | 2.5 mm |
| What movement has the middle node (clamp)? | The system is designed to have a great level of freedom. Depending on the positioning of the pins and the length of the rods the middle node (clamp) can be linked to each rod segment and a 360° orientation |
| Question | Answer |
| In young patients, do you prefer plating or nailing for better reduction? | Galaxy Shoulder Fixation System is a tool for fixation not for reduction. Being a tool for fixation, we cannot blame it for a bad reduction. Similarly, when we face bad reductions after fracture fixation with a plate or a nail, we blame the surgeon and not the tool. For the same reason, our KOLs suggest an open reduction and a percutaneous fixation if the reduction is not satisfactory after closed manoeuvres |
| In which type of fractures do you find most difficult to decide between intramedullary nailing and external fixation osteosynthesis? | KOLs have abandoned other fixation devices, confident by their results using the external fixator. Having said that, in case of fracture of 1 cm distal to the surgical neck, they would consider a plate or a nail because it is difficult to insert the 2 oblique pins when the fracture is too distal. |
| The plate is more investigated with greater blood loss compared to a minimally invasive approach, but rapid mobilisation is provided anyway. What do you think about it? | In our KOLs experience, the average old patient affected by 3 to 4 part PHF, treated with a plate or a nail, does not resume the activity of daily life very soon, despite surgeon post-op suggestions. In young patients, it is easier regardless of the tool you might use. The limiting factor is usually the pain. Our KOLs belief, supported by some experience coming from hospitals that are still using plate along with the external fixator, is that the treatment with the external fixator could provide a faster return to activity of daily life due to less pain and stiffness. |
| Are there review articles about this approach? If so, what are their conclusions vs plating, nailing, pinning? | There are no studies available yet comparing all different techniques |
| What kind of complications have you had? | KOLs had some complications with this technique, such as avascular necrosis or non-union. The benefit of this technique is that the majority of the potential complications can be treated conservatively. The proof of that lies in our rate of revision surgery, only 3% (Follow-up Ranging from 2 to 12 Years). |
| Have you ever experienced pin tract infection? | Our KOLs rate of pin tract infection is around 8%. All these infections were treated by 7 to 14 days of oral antibiotics. None of the pin tract infections evolved in a deep infection. In none of the cases they changed their plan due to a pin tract infection, including earlier removal of the infected pin. |
| In your experience have you never had a case of osteonecrosis after this treatment? | Yes. Our KOLs rate of AVN (at a minimum follow up fo 2 y) is under 4%. Rarely these patients required additional surgery, due to the absence of metalware like locking screws causing glenoid erosion and pain |
| Have you ever had loss of reduction in osteoporotic humeral heads? If yes, which is the rate? | The loosening or backing out of the threaded wires is an extremely rare event. Our KOLs did record this complication but only in 2 patients that the night of the surgery, fell from the bed, during a severe episode of delirium. For this reason, they have learned to contraindicate this technique to patients with very poor compliance or suffering severe neurological disease, which puts them at risk of early fall. They never did a second surgery for loss of reduction, by using this technique. This is also true for patients affected by poor bone quality in which loss of reduction is an extremely rare event. Theoretically, this complication, can be managed either by re-doing the fixation with the external fixator (if the surgeon believes that the fixator was placed in a suboptimal position) or changing fixation device. In this regard, Dr Blonna does not think that changing the device gives better biomechanical advantages than an external fixator placed correctly. Moreover, the great benefit of a temporary device, such as the Galaxy Shoulder Fixation System, is that the patient can cope easily with a minor degree of secondary displacement because after 40 days the ex-fix is removed with no risk of screws cutting out and erosion of the glenoid. |
| What do you do in case of secondary displacement? how often do you do a check x-ray? | Since KOLs have introduced the “pins-bridging technique” they haven’t recorded any significant secondary displacement. This positive outcome is probably the combination of several factors, including the good biomechanical features of the dedicated external fixator, the right selection of the patients, and the surgeon’s experience. A secondary displacement of the fracture should anyway have a similar treatment of another fixation tool. If an early failure is thought to be related to a wrong technique (bad reduction, pins badly positioned in the humeral head, etc), the surgeon can try to apply again the external fixator correcting the technique. If the failure is related to the patient, i.e. recurrent trauma with a secondary displacement of the fracture, they recommend conservative treatment. |
| During treatment, have oblique wires ever migrate into the shoulder joint? | No. Since the external fixator is removed around 40 days from the surgery, the migration of the wires in the joint can’t occur. The mobilization of the wires was much more common in the other direction (with wires backing out and loosening of the reduction) by using standard K-wires without external fixator. After the introduction of the dedicate external fixator threaded wires we solved completely this otherwise common complication. |
| Have you ever had fracture sequelae with this treatment? | Our KOLs had some complications with this technique. The benefit of this technique is that the majority of the potential complications can be treated conservatively. The proof of that lies in our KOLs rate of revision surgery, only 3% (Follow-up Ranging from 2 to 12 Years) |
| What is your rate of union vs non-union and delayed union? | Non-union rate 0.5% (1 case). AVN 4%. Revision surgery rate 3%. |
| Have you experienced any conversions to e.g. plating or replacement? Any infectious complications? | KOLs have limited experience of intraoperative conversion to a reverse replacement. The rate of infection is probably higher than a reverse replacement in a pristine shoulder. For this reason, they recommend, in the most complicated cases, to start directly with open reduction, without the use of any percutaneous pins. If the surgeon is able to obtain a temporary satisfactory reduction, he/she can proceed with the percutaneous fixation. If this is not the case, the surgeon is suggested to change the indication as soon as possible. |
| Have you had any cases of chondrolysis or glenohumeral arthrosis related to the intrarticular wires? | No |
| What about articular glenoid impingement or condral damage of first two humeral head distal pins extremity? | The surgeon must check the length of the pins. There are ways that can guarantee the safety of this procedure. First of all the surgeon must check visually the length of the pins putting the shoulder in internal and external rotation. Secondly, after the insertion of pins, the surgeon has to move the shoulder and detect any clue of protruding pins (crepitus, locking etc etc). In the worst scenario, the surgeon fails to detect a protruding pin, but considering that after 6 weeks everything is removed, the risk of damaging the glenoid is very low and probably not clinically relevant. |
| Which is the patients’ feedback about the external fixator on their shoulder ? Before the surgery, just after the surgery ? | KOLs spend quite an amount of time before surgery explaining to the patient the benefits of the external fixator. A well-prepared patient is the key for a good compliance with the post-op recovery. The majority of the patients understand that 6 weeks of external fixator is a cheap price to pay compared to the very low complication rate, especially the very low revision rate. At follow up examination, it is uncommon that patients report the 6 weeks of life with the external fixator as a very bad experience. |
| Is it effective for osteoporotic bone? | The “pins-bridging fracture technique” and the Galaxy Shoulder external fixator have been designed to be used regardless of the quality of the bone. Thanks to the concept of bi-cortical fixation and to an external fixator dedicated to the treatment of proximal humeral fracture, satisfactory outcomes can be achieved in either young and old patients. This is also true in case of patients affected by poor bone quality where loss of fracture reduction is an extremely rare event. |
| What is the longest time you can wait to fix a fracture with external fixation? Is 14 days too long? | It depends on the fracture. If the fracture is unstable and a secondary displacement is diagnosed at 2/3 weeks from trauma, an attempt for closed reduction and fixation with Galaxy can be performed. If closed reduction is not achievable, a good solution is always an open reduction followed by a percutaneous fixation using the Galaxy. |
| Do you have a patient protocol ? | Wound care once a week. In young patients, KOLs suggest an early rehabilitation, starting with passive ROM immediately after surgery and removing the sling according to the pain. In old patients with complex fractures, KOLs suggest a more conservative rehab protocol. If this is the case, KOLs suggest a gentle pendulum exercises a few days after surgery, but active ROM is recommended only after the removal of the external fixator. If the surgeon is in doubt about when starting passive and active ROM after surgery, the opinion of the developers of the Galaxy Shoulder Fixation System is that a delayed rehab, in their long experience, does not affect negatively the final outcome. So, if in doubt, do not push too much on early rehabilitation. |
| Is it immediately possible to mobilize the arm after surgery? | In young patients, KOLs suggest an early rehabilitation, starting passive ROM immediately after surgery and removing the sling according to the pain. In old patients with complex fracture, KOLs suggest a more conservative rehab protocol. If this is the case, we can start with gentle pendulum exercises a few days after surgery, but active ROM is recommended after the removal of the external fixator. If the surgeon is in doubt about when starting passive and active ROM after surgery, the opinion of the developers of the Galaxy Shoulder Fixation System is that a delayed motion, in their long experience, do not affect negatively the final outcome. So, if in doubt, do not push too much on early rehabilitation. |
| How long do your patients wait for starting rehabilitation? | A self-assisted pendulum exercise is started as soon as possible (usually 5 to 7 days after surgery). A formal rehab program, with a physiotherapist, is usually started 3 to 4 weeks after surgery. Younger patients start the rehab program 10 days -2 weeks after surgery. |
| Do you change wrappings and how do you clean the pins? | Wound care once a week |
| Could it be useful to remove only greater tuberosity wires at week 4? | This can be an option to speed up rehabilitation or to solve pins tract infection, but our KOLs don’t have experience in this practice. |
| Have you ever faced damages to axillary nerve with this technique? | Not with the last version of our “pins bridging fracture technique”. With the old technique, in which KOLS adopted more oblique wires, they observed one temporary partial palsy, that resolved within 6 months follow up |
| What is the average length of surgery time? | In our KOLs experience, the majority of surgeries last less than 1h. The easiest cases can be treated in 20 minutes. |
| Is it mandatory to perform the reduction with close manoeuvers? | In case of 4-part proximal humeral fracture, KOLs recommend an open reduction. In case of 3-part proximal humeral fracture and 2-part proximal humeral fracture, the type of reduction depends on what the surgoen is achieving by closed manoeuvers. If he obtains a satisfactory reduction of the fragments by closed manoeuvers, this would give better cosmesis, less pain and less deep infections than a standard open procedure. If the reduction is not satisfactory after an attempt for closed reduction, KOLS’ threshold to change from closed to open is very low. In simple terms, a satisfactory open reduction is better than an unsatisfactory closed reduction. The open reduction and percutaneous fixation by using the Galaxy Shoulder Fixator technique increase the rate of deep infection compared to closed reduction but not compared to a standard open reduction and internal fixator by using a plate or nail. These data have been published in a multicentre study. |
| Do you use wires to help reduction? | This option can be used to improve the quality of the reduction. However, the threaded wires are not designed to support aggressive reduction manoeuvers. Moreover, the quality of the bone at the level of the greater tuberosity can determine the fragmentation of the greater tuberosity during reduction manoeuvers. KOLs suggest not to use this technique routinely. |
| Is it always helpful to dis-impact the humeral head in three part valgus impacted fractures? | Our aim is to obtain a good reduction of the humeral head. Valgus impacted proximal humeral fractures usually are associated with satisfactory results after conservative treatment. If surgical treatment is indicated, the surgeon should aim for a reduction of the humeral head. |
| How do you maintain the reduction during first wire insertion? | Usually, keeping the patient’s arm still is enough to avoid intraoperative displacements. This is true especially in the case of 2 part PHF after closed reduction. In the case of an open procedure, the reduction is maintained by the blunt instrument. To reduce the time lapse between reduction and fixation KOLs prefer to start preparing the two obliques pins even if the head is still displaced. When the pins are in place, the reduction of the humeral head is immediately followed by the further insertion of the two pins. In this way the risk of intraoperative displacement is extremely low. |
| Why not using a first proximal pin percutaneously to do a close reduction before ascendant pins? What about lesser tuberosity fixation? | If the fracture is very unstable (a not very common event) and the patient is not fat or muscular, the 2 proximal pins can be used to reduce the humeral head or/and the GT. However the pins are not designed for this purpose. The surgeon should be aware of the potential breakage of pins. Moreover, a bent pin is difficult to be removed without anestesia. The lesser tuberosity, if displaced (not just broken) is reduced and fixed with osteosutures using a deltopectoral approach |
| How far from the fracture do you have to insert distal wires? | Our KOLs suggestion is 2 to 4 centimeters distal from the oblique pins. Avoiding to stay too close to the oblique pins should limit the risk of iatrogenic fracture |
| In the case of 2-3 fragments, would it have been better to put a plate and still run an open access for fracture reduction? | Dr Blonna has just published a paper on JBJS in which his rate of revision surgery (of any type) is below 5%, with a minimum follow up of 2 years. Approximately half of the patients suffered of 3-4 part PHF -hence difficult cases. Despite he didn’t have a control group treated with a plate, the literature suggests that the revision rate using plates is higher than 10%. Strong of his experience and data, he has stopped using plates for 10 years. |
| To treat a 3 part proximal humeraus fracture (but even 2 part) with the common varus and posterior head comminution, the close reduction is performed in ABD and RE, pushing the diaphysis posteriorly. The introduction of the wires in such position, kept by an assistant, follows always the same procedure: 1 cm anteriorly to the middle line of the humerus and 9 cm distally the lateral edge of the acromium? | Of course it’s not easy. The best way to insert the oblique wires is relying on the landmarks and aiming posteriorly. If a good reduction has been achieved, the humeral head will be 20°-30° in a retroversal position.In case of doubt, inserting the pin more anteriorly will allow to get a better posterior position. The coracoid is another reference point. In normal conditions, the coracoid point shuould be projected in the middle of the humeral head. Once got the reduction, it is possible to keep the shoulder in a more phyological position and not in ABD and ER. Usually our KOLs keep the shoulder in a neutral position at 20°-30° of abduction. |
| In case of fracture with more fragments in which you choose orif, do you also use osteosutures in addition to the pins? | Yes, our KOLs normally link GT and LT together with number 2 non-absorbable sutures |
| Is it possible to add other pins if fracture requires? | Yes it is possible. The external fixator can be used as well. This was a common event in our KOLs early experience. The principle of using only 6 pins, is to propose a standardized and reliable technique. If the surgeon is not sure about the position of one of the pins, an additional pin can be placed. On the contrary, we discourage surgeons to use less than 6 pins. |
| After how many minutes do you decide to “switch” to open reduction? | In case of a true 4-part proximal humeral fracture (lesser tuberosity is displaced not only fractured), KOLs recommend an open reduction without an attempt for closed reduction. In case of 3-part proximal humeral fracture and 2-part proximal humeral fracture, the type of reduction depends on what we are achieving by closed manoeuvers. If by closed manoeuvers the surgeon obtains a satisfactory reduction of the fragments this would give better cosmesis, less pain and less deep infections than a standard open procedure. If the reduction is not satisfactory after an attempt for closed reduction, our KOLs threshold to change from closed to open is very low and they swift to an open reduction in about 10 to 20 minutes usually. |
| Which is the percentage of open reduction when using this product? | In case of a true 4-part proximal humeral fracture (lesser tuberosity is displaced not only fractured), KOLs recommend an open reduction without an attempt for closed reduction. In case of 3-part proximal humeral fracture and 2-part proximal humeral fracture, the type of reduction depends on what we are achieving by closed manoeuvers. If by closed manoeuvers the surgeon obtains a satisfactory reduction of the fragments this would give better cosmesis, less pain and less deep infections than a standard open procedure. If the reduction is not satisfactory after an attempt for closed reduction, our KOLs threshold to change from closed to open is very low and they swift to an open reduction in about 10 to 20 minutes usually. |
| Which is the percentage of open reduction when using this product? | In our KOLs last report on JBJS on 188 patients, the reduction was performed with percutaneous manoeuvers in 120 shoulders (63.8%) and with delto-pectoral approach in 68 cases (36.2%). |
| Could you perform surgery with local anesthesia or neural block? | In old patients with comorbidities the anesthesiologists prefer peripheral block instead of general anesthesia. This is especially true in case of 2 part PHF, in which the risk of intraoperative conversion to a replacement is extremely low. |
| How long is X-ray exposure for a complete surgery? | The exposure to X-rays depends on several factors including the type of fracture and surgeon skills. A simple 2 part proximal humeral fracture required less than 20 seconds. The most difficult cases usually less than 1 minute. The open procedure reduces substantially the amount of X-rays. |
| Do you never control the profile on X ray? (except with rotation)? | Maximum internal rotation and external rotation are more than enough to be sure about reduction and length of pins. |
| Do you prefer lateral or Beach chair position? | Beach chair position. |
| What are the real advantages of using external fixation? | 1) It is a temporary fixation so lower risk of delayed complications related to hardware. 2) Mini-invasive technique (periosteum is kept intact with a better chance of rapid healing of the fracture). Soft tissue envelopment, including periosteum, is less damaged by the surgeon providing an intrinsic increase of the stability of the fixation. 3) It allows a bi-cortical fixation, something that is not achievable with other techniques. 4) The two proximal threaded wires in the head are placed to work as a buttress against varus displacement. No other systems have screws that can be placed in the same direction as the 2 proximal wires of our technique. |
| Is there a standard way to connect the 6 wires together? | Yes, the technique is reported in the official brochure. Having said that, changes can be done in order to connect the 6 wires. The concept is that all threaded wires have to be linked to the rods. |
| Is the fixator compatible with magnetic resonance? | No, it isn’t |
| Which is the diameter of the K. wires? | 2.5 mm |
| What movement has the middle node (clamp)? | The system is designed to have a great level of freedom. Depending on the positioning of the pins and the length of the rods the middle node (clamp) can be linked to each rod segment and a 360° orientation |
About Orthofix
Orthofix Medical Inc. is a global medical device and biologics company with a spine and orthopedics focus. The Company’s mission is to deliver innovative, quality-driven solutions as we partner with health care professionals to improve patient mobility
- Blonna D et al. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019 Sep 18; 101(18):1654-1661.
- Pekka Kannus, Mika Palvanen, Seppo Niemi, Harri Sievänen, Jari Parkkari. Bone. Rate of proximal humeral fractures in older Finnish women between 1970 and 2007. Volume 44, Issue 4, April 2009, Pages 656-659.